
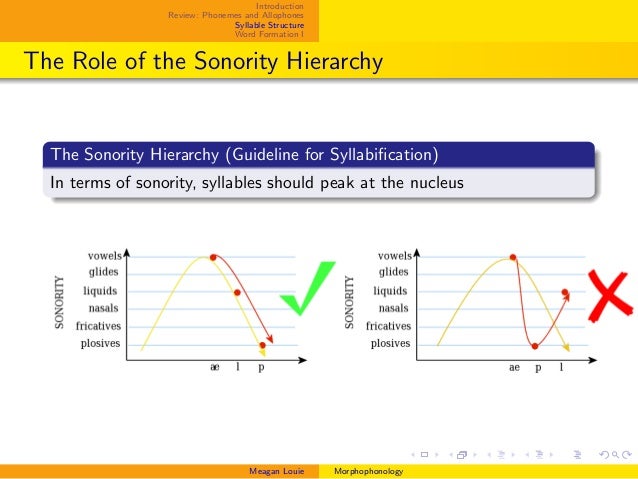
Syllables which have branching anywhere within the rhyme constituent is called a heavy syllable. Evidence for this: V type syllables appear first in human children s speech aphasia patients start using V type syllables first as they recover languages which have both onset and coda consonants typically allow a wider range of consonants in the onset position coda consonants are much more likely to undergo loss of articulation in the course of historical development there are no known languages which have V-type syllables but lack V-type syllables but the reverse is not the case of 7ħ Therefore the syllable structure of appraise /.p eiz/ is: x x x x x x p e I z V V Syllable Weight Syllables in which there is no branching within the rhyme, either at the level of rhyme node itself or within the nucleus is called a light syllable. Therefore appraise is /.p eiz/ Maximum onset principle is connected with the universal fact about syllable structure that (in some sense) V syllable structure is more basic than V types. eiz/ The principle of maximum onset says that in cases like this, where the language specific phonotactics will allow for two or more syllabifications across a syllable boundary, it is the syllabification which maximizes the material in the following onset that is preferred. What we must decide then is whether the syllabification of appraise is /.p eiz/ or / p. of 7Ħ Therefore, /u p /, /sip / are ill-formed. We know: /p/ may occur in coda position in English (cap, cup ) /p / is a well-formed onset in English (prize, preen ) / / may occur alone in onset position (rice, raze ) / p / is not a well-formed coda cluster as it violates the predictions of the sonority hierarchy. Maximal nset Maximal onset principal is also considered a universal principle of syllabification In a word like appraise - / p eiz/, it is clear that the word is bisyllabic the question is where the boundaries are. sprint - /sprint/ However as it is this -initial consonant cluster (which is also the only three-way branching onset in English) that violates the sonority hierarchy predictions, the principle is considered a universal one. blink - /blik/ This principle runs into some difficulty in syllables with consonant clusters involving an initial s e.g. Applied to syllable structure, the idea is that the most sonorous element in a syllable will be located within the nucleus, and that the further one gets from the nucleus, the less sonorous are the segments. it is claimed that sequences of segments are syllabified in accordance with a sonority scale of the following form: Low vowels High vowels Sonority Approximants asals Voiced fricatives Voiceless fricatives Voiced stops Voiceless stops Sonority of increases from the bottom to the top of the scale Sonority is an acoustic effect the more sonorous a sound the more it resonates. There are two main universal constraints: 1. constraints on the syllabification of sequences of segments. of 7Ĥ The Sonority Hierarchy It is widely believed that there are both universal and language specific constraints on the form that syllables may take i.e. they occupy a single unit of timing) while having an internal structure which resembles two segments. chips /tsips/ x x x x t S I p s V Segments such as and are called complex segments, since they behave like single segments (i.e.
Using the same principle, the use of the skeletal tier enables us to identify the different consonant properties of affricates: e.g. The point is that nuclei with long vowels and with diphthongs are parallel with respect to the number of timing slots within the nucleus. bit - /bit/ x x x b I t V of 7Ģ bee /bi / x x x b i V buy /bai/ x x x b a I V of 7ģ What is intended by the representations above is that long vowels are constituted as a single vowel quality which is attached to two skeletal slots whereas diphthongs have two different vowel qualities. In order to do this, the nucleus is branched and short vowels are represented on a single tier while long vowels (including diphthongs in English) are represented as occupying two tiers. Such distinctions are represented by attaching the segments of the syllable into timing slots referred to as the skeletal tier.

We have not, for example, represented the difference between short and long vowels. 1 SYLLABLE & SYLLABLE STUTUE (continued) The syllables we have looked at so far are fairly simple ones.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
